
Financing is the process of providing funds for business activities, investing etc. Financial institutions, such as banks, are in the business of providing capital to businesses and investors to help them achieve their goals. An entity can raise money through Corporate Finance or Project Finance depending upon the scope of work. If the new initiative is Financed based on the strength of the balance sheet, using the assets, cashflows and good will of company as collateral to guarantee the additional credit provided by lenders,
it is called Corporate Finance. If the project is not successful, all the remaining assets and cash flows can serve as a source of repayment for all the creditors. In Project Financing, the new project is incorporated into a newly created economic entity, the SPV and financed off balance sheet. Existing firm is not liable for the failure of the project. Project Finance is the structured Financing of a specific economic entity—the SPV, or special-purpose vehicle, also known as the project company—created by sponsors using equity or mezzanine debt and for which the lender considers cash flows as being the primary source of loan reimbursement, whereas assets represent only collateral.
| Factor | Corporate Financing | Project Financing |
|---|---|---|
| Guarantees for financing | Assets of the Borrower. | Project quality and soundness of the financial feasibility of the Project. |
| Financial Elasticity | Impacts the financial elasticity of the borrower. | No effect or heavily reduced effect on theSponsors. |
| Accounting Treatment | On the balance sheet. | Off the balance sheet (Apart from disbursement to subscribed equity or subordinate loans). |
| Key factors impacting financing | Customer relationships, Profitability, Strength of the balance sheet | Future cashflows of the Project. |
| Basis of Leverage | Depends of strength of the balance sheet of the borrower. | Depends on the cashflows generated by the Project. |
| Risk | Risk of the Project is entirely borne by the Sponsor. | Risk of the Project is spread among various Sponsors and entities involved. |
| Cost of Financing | Lower costs compared to the Project financing option. | Transaction costs ~ 5–10% of total investment. |
The major differences between corporate and Project Financing are:
While the sponsors of the project finance the SPV using equity, a major part of funds required for the project are raised through debt. Debt Sizing and debt sculpting are the two major factors that determine the size of the debt and the nature of repayment.
Please click here to know more about Project finance.
Debt Sizing:
The debt sizing helps to determine the maximum amount of debt that can be raised to support infrastructure project. Typically, a banker provides a term sheet listing the Loan to Cost/ Value and the ratios like DSCR (Debt Service Coverage Ratio) and LLCR (Loan life coverage ratio) - that the project SPV needs to maintain while servicing the debt.
Where it is used:
The Term Sheet will define the DSCR which is one of the core drivers of the debt sizing for the project and assesses the ability of the project to repay its debt. The debt repayments need to match the cashflow profile to avoid having periods where there is not enough actual cashflow to repay the debt.
If a lender wants the SPV to maintain the target minimum DSCR to obtain a BBB–rating to be 1.4 using base case cash flow. Using the cashflows of down side scenario, if the lender arrives at DSCR of 1.2, the lender may then choose the lower debt size resulting from the two different debt-sizing calculations. Project finance transactions often also have a debt leverage constraint. If the debt size results in a high leverage such as 80 percent, then the debt size is limited to a number usually driven by industry averages.
How to compute:
We would be required to rearrange the DSCR ratio as under:
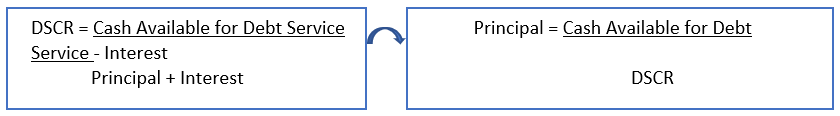
We need to set up a financial model for principal repayments based on the expected DSCR on such leverage. Calculating Interest on debt and reducing the same from the debt service. Use the NPV formula to derive the maximum debt the lender can sponsor. You can download an open-source model for your understanding.
Debt Sculpting
Debt sculpting is process matching debt service with the available Cash flow available for Debt service.
It requires the principal repayment obligations to be calculated to ensure that the debt service obligations are appropriately matched to the strength and pattern of the cash flows in each period.
Where it is used:
Debt sculpting is applied when a project has irregular cash flows, for example:
- in oil & gas projects,
- or because of the seasonal demand factors, which is common in the power and water industry,
- or because of an unusual but expected payment, such as a major overhaul of an asset
How to compute:
The lender would want to assess the project’s ability to match with a minimum DSCR ratio. If the project achieves this minimum DSCR, it would be acceptable to the lenders. In the project, there is a limited possibility to manoeuvre with Cashflow Available for Debts and Interest payments. However, we can adjust the principal repayments in line with the given DSCR. Another aspect one needs to keep in mind is this constant DSCR leads to 100% repayment of the debt. But this is only half story, we need to test the remaining cashflows from the perspective of equity shareholders and understand is the returns for equity investments is in line with their expectation.
You can download an open-source model for your understanding.
In case of assistance, please get in touch with us at info@centaurireaserch.com.







